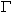 D = 10°C/km is the dry adiabatic lapse rate.
D = 10°C/km is the dry adiabatic lapse rate.
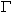 W = 6°C/km is our value for the wet adiabatic lapse rate.
W = 6°C/km is our value for the wet adiabatic lapse rate.
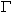 E is the environmental lapse rate which must
be given. On the global average
E is the environmental lapse rate which must
be given. On the global average 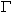 E = 6.5°C/km
E = 6.5°C/km
- The parcel is an imaginary box of air which does not
allow a transfer of heat in or out of the box.
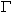 D = 10°C/km is the dry adiabatic lapse rate.
D = 10°C/km is the dry adiabatic lapse rate. 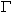 W = 6°C/km is our value for the wet adiabatic lapse rate.
W = 6°C/km is our value for the wet adiabatic lapse rate.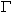 E is the environmental lapse rate which must
be given. On the global average
E is the environmental lapse rate which must
be given. On the global average 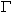 E = 6.5°C/km
E = 6.5°C/km
- Stability is when an object is displaced and returns
to its original position.
Instability is when an object is displaced and it moves
away from its original position. Neutrality is when an object is
displaced and it remains in the new position.
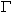 E <
E < 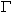 W, then the atmosphere is absolutely stable.
W, then the atmosphere is absolutely stable.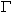 E >
E > 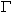 D, then the atmosphere is absolutely unstable.
D, then the atmosphere is absolutely unstable.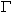 W <
W < 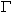 E <
E < 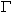 D, then the atmosphere is conditionally
unstable.
D, then the atmosphere is conditionally
unstable.
- Conditional instability means that the air is stable under the
condition that the air is not saturated, and unstable if the air
is saturated.
- The LCL or lifting condensation level is the level
where lifted air saturates; base of clouds.
- The LFC or level of free convection is the level at which lifted air becomes unstable; found at the intersection of the environmental temperature and the adiabatic temperature assuming that above that point the air is unstable.
- The EL or Equilibrium Level is the level at which lifted air can no longer rise due to instability. At this level, the parcel becomes colder than the environment, thus stable again; found at the intersection of the environmental temperature and the adiabatic temperature assuming that above that point the air is stable and below that point, unstable.